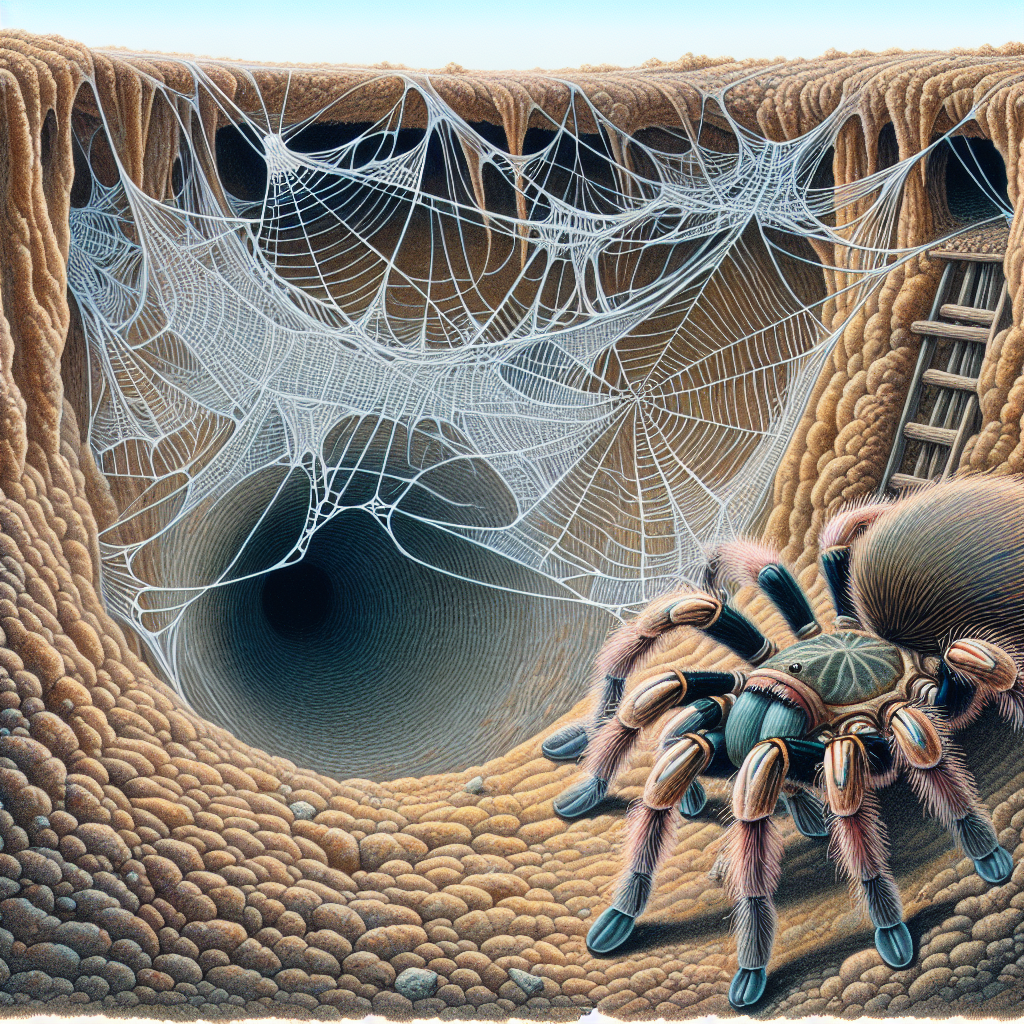
Have you ever wondered if there are any burrowing tarantula varieties known for their intricate tunneling behavior? Well, you’re in for a treat because in this article, we will explore the fascinating world of burrowing tarantulas and their ability to create elaborate tunnels. From the depths of their underground hideouts to the complex network of tunnels they construct, these tarantulas are truly remarkable creatures. So, buckle up and prepare to delve into the extraordinary world of these captivating arachnids.
Burrowing Tarantula Varieties
Introduction to burrowing tarantulas
Burrowing tarantulas are a fascinating group of spiders known for their ability to construct intricate tunnels beneath the surface of the earth. These arachnids have evolved unique adaptations and behaviors that allow them to thrive in underground habitats. By studying their tunneling behavior, scientists can gain valuable insights into spider behavior, ecology, and evolution.
Characteristics of burrowing tarantulas
Burrowing tarantulas possess several distinguishing characteristics that enable them to excel in their subterranean lifestyle. These spiders typically have robust bodies and strong legs, which aid in digging through soil and creating elaborate burrows. They also have strong jaws and venomous fangs, which they use to capture and subdue their prey. Additionally, burrowing tarantulas often have dense, hairy bodies that help protect them from predators and regulate their body temperature.
Importance of studying tunneling behavior
Understanding the tunneling behavior of burrowing tarantulas holds great significance in various fields of research and conservation. By investigating how tarantulas construct their burrows, scientists can gain insights into their habitat preferences, resource acquisition strategies, and interactions with other organisms. Furthermore, studying tunneling behavior can enhance our knowledge of spider evolution and provide essential information for the conservation of these unique arachnids.

Tarantula Species Known for Intricate Tunneling
Giant Blonde Tarantula
The Giant Blonde Tarantula (Aphonopelma chalcodes) is a species native to the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. It is renowned for its complex tunneling behavior, with burrows often reaching impressive depths of several feet. These burrows serve as multifunctional structures, providing shelter, protection, and a place for molting and egg-laying. The Giant Blonde Tarantula’s tunneling behavior highlights its ability to adapt to its arid habitat and underscores the importance of studying such behaviors for conservation efforts.
Mexican Red Rump Tarantula
The Mexican Red Rump Tarantula (Brachypelma vagans) is a species found primarily in Mexico and parts of Central America. This tarantula is known for its intricate burrow architecture, which exhibits a unique combination of complexity and simplicity. While some individuals construct shallow, simple burrows, others create elaborate networks of tunnels with multiple chambers. Factors such as substrate type, humidity levels, and availability of prey are thought to influence the complexity of their burrows, making the Mexican Red Rump Tarantula an intriguing subject for further study.
Brazilian Cave Tarantula
The Brazilian Cave Tarantula (Speocera brasiliensis) is a species that inhabits dark cave systems in Brazil. It displays a fascinating contrast in tunneling behavior, with some individuals constructing shallow burrows near cave entrances, while others venture deeper into the darkness, creating intricate networks of tunnels. This variability in burrow structure suggests a remarkable level of adaptability to different environmental conditions and prey availability. Exploring the tunneling behavior of the Brazilian Cave Tarantula provides valuable insights into the interplay between burrow structure and prey capture strategies in cave-dwelling tarantulas.
Chilean Rose Tarantula
The Chilean Rose Tarantula (Grammostola rosea) is a species native to Chile and Argentina. Unlike some of its burrowing counterparts, this tarantula exhibits limited tunneling behavior, often preferring to create simple, shallow burrows. This species represents an interesting contrast to other burrowing tarantulas, as it highlights the diverse range of tunneling behaviors among tarantula species. By comparing the tunneling habits of the Chilean Rose Tarantula with those of other burrowing tarantulas, researchers can gain valuable insights into the factors influencing variation in tunneling behavior within this group of arachnids.
Mexican Flame Knee Tarantula
The Mexican Flame Knee Tarantula (Brachypelma auratum) is a species native to Mexico. It stands out among its burrowing counterparts due to its unique tunneling behavior, characterized by the creation of intricate, labyrinthine burrows. These tunnels feature multiple entrances, chambers, and even false exits, making them highly complex structures. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and availability of prey are believed to contribute to the development of these intricate burrows. The Mexican Flame Knee Tarantula’s tunneling behavior provides a captivating avenue for research on the adaptations and strategies employed by tarantulas to create and navigate complex underground networks.

Comparative Study of Tunneling Behavior
Factors affecting tunnel complexity
Research has revealed that various factors influence the complexity of burrowing tarantula tunnels. Soil consistency, temperature, humidity levels, and prey availability all contribute to the diversity of burrow structures observed among different species. Furthermore, individual behavior and genetic predispositions may also play a role in shaping tunnel complexity. Understanding these factors can shed light on the environmental and biological factors that drive tunneling behavior in tarantulas.
Variations in burrow type and structure
Burrowing tarantulas display a wide range of burrow structures, from simple, shallow depressions to extensive networks of interconnected tunnels. Their burrows can vary in depth, width, number of chambers, and overall complexity. By comparing and contrasting the different types of burrows constructed by various species, researchers can uncover important insights into the adaptive significance of tunneling behavior and the ecological role of burrows in the lives of tarantulas.
Influence of environmental conditions
Environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and substrate type have a significant impact on the tunneling behavior of burrowing tarantulas. For example, species inhabiting arid regions may create deeper burrows to access moister soil or regulate their body temperature. The influence of environmental conditions on tunneling behavior highlights the nuanced relationship between arachnids and their habitats and underscores the need for a comprehensive understanding of these factors when studying tarantula behavior.
Implications for understanding spider behavior
The study of tunneling behavior in burrowing tarantulas provides valuable insights into the behavior and ecology of spiders as a whole. By investigating the mechanisms and strategies employed by tarantulas to construct and utilize tunnels, researchers can enhance their understanding of spider behavior, resource acquisition, and predator-prey interactions. Additionally, these studies contribute to the broader field of spider research, offering comparative perspectives and allowing for the exploration of broader evolutionary patterns and ecological implications.

Importance of Tunneling Behavior Research
Ecological significance
Tunneling behavior in burrowing tarantulas plays a crucial role in shaping their local ecosystems and influencing the distribution and abundance of other organisms. Tarantula burrows serve as shelter and nesting sites for various invertebrates, reptiles, and small mammals, creating microhabitats within the soil. By studying the tunneling behavior of tarantulas, scientists can gain insights into the ecological connections and impacts of these arachnids, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of ecosystem dynamics.
Insights into spider evolution
Burrowing tarantulas represent an ancient lineage of spiders, and the study of their tunneling behavior provides valuable insights into the evolution of spiders as a whole. By examining the adaptations and behaviors associated with burrowing, researchers can trace the evolutionary pathways that have led to the diverse range of spider species and their respective ecological niches. Tunneling behavior research offers a window into the long evolutionary history of spiders and the selective pressures that have shaped their behaviors and ecological roles.
Conservation implications
Understanding the tunneling behavior of burrowing tarantulas has important implications for the conservation of these unique arachnids and their habitats. By identifying and characterizing tarantula burrows, researchers can gain a better understanding of the species’ distribution, abundance, and response to environmental changes. This knowledge can guide conservation efforts, aid in the assessment of habitat suitability, and contribute to the development of effective management strategies for protecting and preserving burrowing tarantulas and their ecosystems.
Practical applications
The study of burrowing tarantula tunneling behavior has practical applications beyond purely scientific endeavors. For example, understanding how tarantulas construct their burrows could inform engineering and construction practices related to underground structures. The unique adaptations and behaviors observed in tarantulas may inspire innovative solutions for tunneling technology or mining practices. By recognizing the practical implications of tunneling behavior research, we can bridge the gap between scientific knowledge and real-world applications.
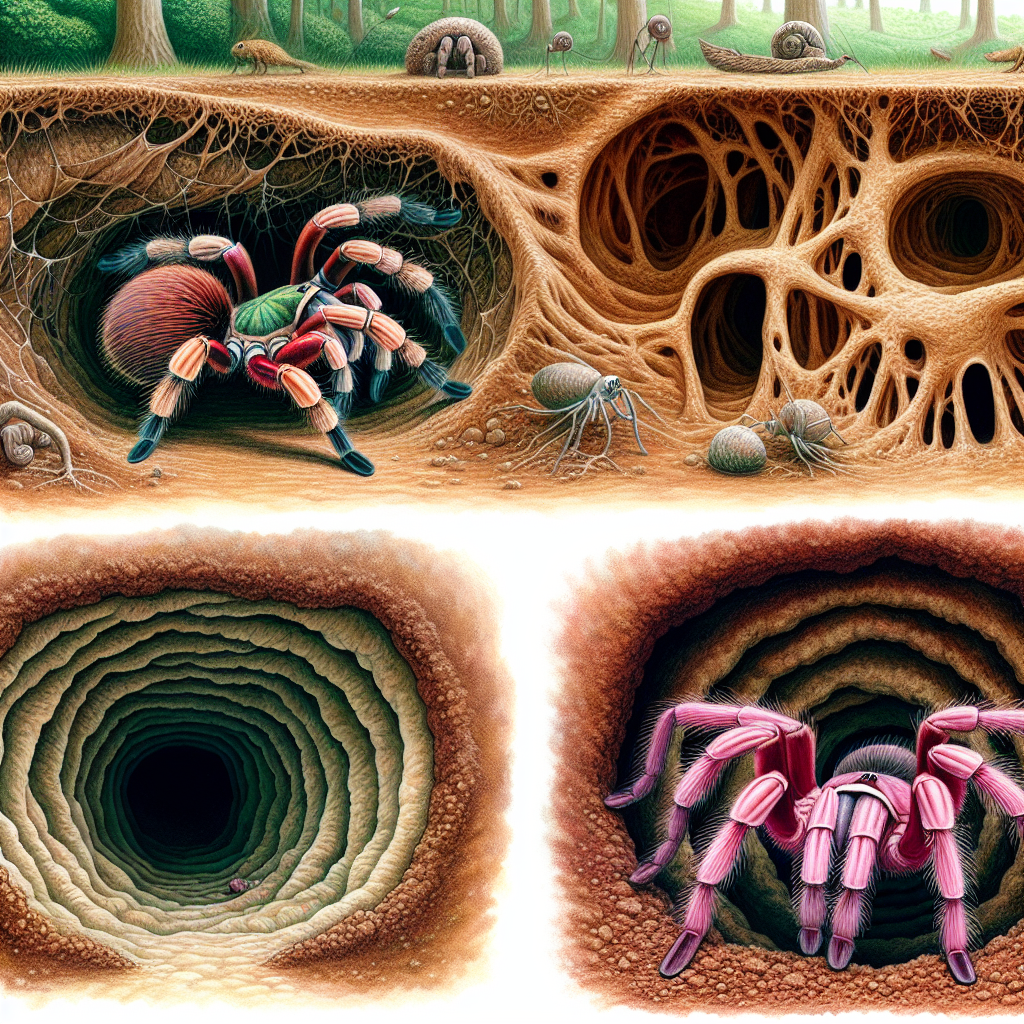
Conclusion
In conclusion, burrowing tarantulas exhibit a rich diversity of tunneling behaviors, ranging from simple, shallow burrows to complex underground networks. The Giant Blonde Tarantula, Mexican Red Rump Tarantula, Brazilian Cave Tarantula, Chilean Rose Tarantula, and Mexican Flame Knee Tarantula represent remarkable examples of this diversity, each with its own unique tunneling adaptations and behaviors. Comparative studies of tunneling behavior in burrowing tarantulas offer valuable insights into the factors influencing tunnel complexity, the ecological significance of burrows, spider evolution, and conservation implications. By appreciating the complexity of tarantula behavior and conducting further research in this field, we can unlock the secrets of these fascinating arachnids while also contributing to broader scientific knowledge and practical applications.